ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miners are specialized hardware designed to perform cryptocurrency mining with unparalleled efficiency. However, their high computational power generates significant heat, making cooling systems critical to maintaining performance, longevity, and energy efficiency. This report explores the design principles, types, challenges, and innovations in ASIC miner cooling technologies.
The Importance of Cooling in ASIC Mining
ASIC miners operate 24/7 under heavy workloads, causing chips to reach temperatures exceeding 80°C. Excessive heat degrades hardware components, reduces hash rates, and increases the risk of catastrophic failure. Effective cooling stabilizes operating temperatures, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing downtime. Additionally, efficient thermal management reduces energy consumption, a key factor in profitability for large-scale mining operations.
Types of ASIC Miner Cooling Systems
1. Air Cooling
Air cooling is the most widely used method due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. It relies on heatsinks and fans to dissipate heat. Heatsinks, often made of aluminum or copper, absorb heat from ASIC chips, while fans blow air across their fins to accelerate heat transfer.
- Advantages: Low upfront cost, ease of maintenance, and compatibility with most ASIC models.
- Disadvantages: Limited efficiency in high-density setups, noise pollution from fans, and dependency on ambient temperatures.
Some miners use “push-pull” fan configurations, where one fan forces air into the heatsink, and another exhausts it, improving airflow. However, dust accumulation in vents remains a persistent issue, requiring regular cleaning.
2. Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling systems use coolant fluids to absorb and transfer heat away from ASIC chips. These systems are categorized into two subtypes:
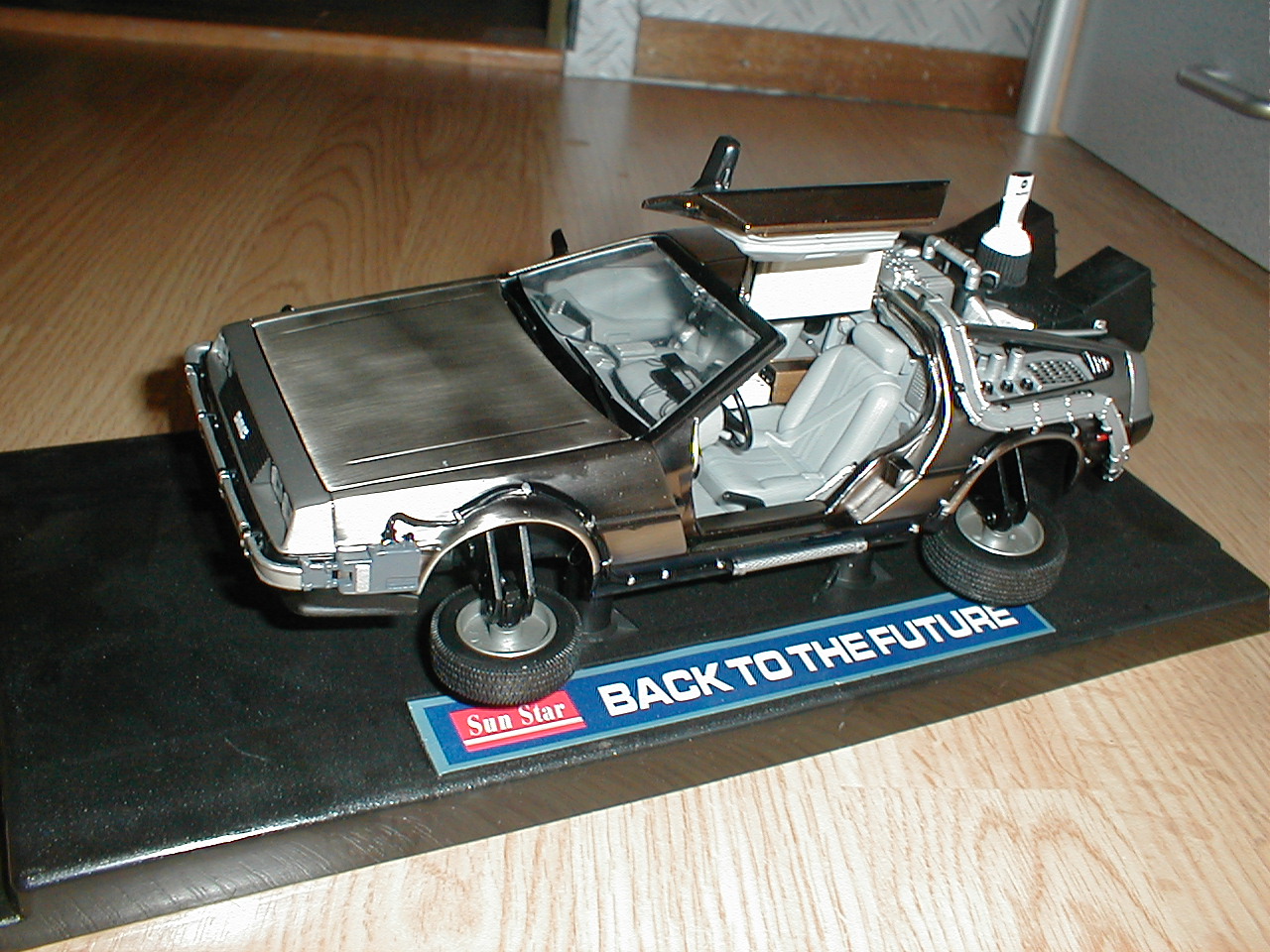

- Closed-Loop Liquid Cooling: Coolant circulates through tubes and a radiator, similar to PC water-cooling setups. Cold plates attached to ASIC chips absorb heat, which is then dissipated via radiators.
- Immersion Cooling: Miners are submerged in dielectric fluid, a non-conductive coolant that absorbs heat directly. This method eliminates fans and heatsinks, relying instead on external heat exchangers to cool the fluid.
- Advantages: Superior heat dissipation, quieter operation, and suitability for high-density mining farms.
- Disadvantages: Higher installation costs, complexity in maintenance, and potential fluid leakage risks.
Immersion cooling, though expensive, is gaining traction in industrial-scale operations due to its energy efficiency and ability to handle overclocked hardware.
3. Hybrid Cooling
Hybrid systems combine air and liquid cooling to balance cost and efficiency. When you have almost any inquiries regarding in which along with how to utilize Bitcoin mining difficulty chart, you possibly can e-mail us on our site. For example, liquid-cooled heatsinks may be paired with low-speed fans to reduce noise while maintaining thermal stability.
Key Components of Cooling Systems
- Heatsinks: Engineered with high thermal conductivity materials like copper or vapor chambers.
- Fans: Axial or centrifugal fans with variable speeds (controlled via PWM) to adjust airflow based on temperature.
- Thermal Interface Materials: Thermal paste or pads ensure efficient heat transfer between chips and heatsinks.
- Heat Exchangers: Used in liquid systems to transfer heat from coolant to the environment.
Challenges in ASIC Miner Cooling
- Heat Density: Modern ASICs pack more transistors into smaller areas, increasing heat generation per square centimeter.
- Energy Consumption: Cooling systems themselves consume power, impacting overall profitability.
- Environmental Factors: High ambient temperatures or humidity reduce cooling efficiency, necessitating climate-controlled facilities.
- Dust and Debris: Accumulation in air-cooled systems obstructs airflow, requiring frequent maintenance.
Best Practices for Effective Cooling
- Regular Maintenance: Clean fans and heatsinks monthly to prevent dust buildup. Replace thermal paste annually.
- Optimal Facility Design: Arrange miners in rows with spaced aisles to promote airflow. Use raised floors for ventilation in data centers.
- Environmental Controls: Deploy HVAC systems to maintain ambient temperatures below 25°C.
- Monitoring Tools: Implement software (e.g., Hive OS, Awesome Miner) to track temperatures and adjust fan speeds dynamically.
- Overclocking Caution: Avoid pushing hardware beyond safe thermal limits without adequate cooling.
Future Trends in Cooling Technology
- Advanced Materials: Graphene-based heatsinks and nanocoatings to enhance thermal conductivity.
- Two-Phase Immersion Cooling: Utilizing phase-change fluids that absorb heat through evaporation, improving efficiency.
- AI-Driven Cooling: Machine learning algorithms to predict thermal loads and optimize fan/pump speeds in real time.
- Waste Heat Recycling: Redirecting excess heat to warm buildings or power absorption chillers, improving sustainability.
Conclusion
ASIC miner cooling systems are pivotal to the viability of cryptocurrency mining operations. While air cooling remains dominant for small-scale setups, liquid and immersion cooling are revolutionizing industrial mining with unmatched efficiency. As ASICs grow more powerful, innovations in materials, AI integration, and sustainable practices will shape the future of thermal management. Balancing upfront costs, energy consumption, and performance will continue to drive advancements in this critical field.

 by brookfay708830
by brookfay708830







Leave a Reply